Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Thermal history analysis (BETA)#
Warning
Beta Features Disclaimer
This is beta documentation for one or more beta software features.
Beta features are considered unreleased and have not been fully tested nor fully validated. The results are not guaranteed by Ansys, Inc. (Ansys) to be correct. You assume the risk of using beta features.
At its discretion, Ansys may release, change, or withdraw beta features in future revisions.
Beta features are not subject to the Ansys Class 3 error reporting system. Ansys makes no commitment to resolve defects reported against beta features; however, your feedback will help us improve the quality of the product.
Ansys does not guarantee that database and/or input files used with beta features will run successfully from version to version of the software, nor with the final released version of the features. You may need to modify the database and/or input files before running them on other versions.
Documentation for beta features is called beta documentation, and it may not be written to the same standard as documentation for released features. Beta documentation may not be complete at the time of product release. At its discretion, Ansys may add, change, or delete beta documentation at any time.
This example shows how to use PyAdditive to determine thermal history during a build using a simulated coaxial average sensor.
Units are SI (m, kg, s, K) unless otherwise noted.
Perform required import and connect#
Perform the required import and connect to the Additive service.
from ansys.additive.core import (
Additive,
AdditiveMachine,
BuildFile,
CoaxialAverageSensorInputs,
MachineType,
Range,
SimulationError,
StlFile,
ThermalHistoryInput,
)
additive = Additive(enable_beta_features=True)
Specify model#
Specify the geometry model. PyAdditive supports two types of geometry
specifications, the StlFile class and the BuildFile class.
You can download the example build and STL files by importing the
examples module.
import ansys.additive.core.examples as examples
# Create an ``StlFile`` object.
stl_name = examples.download_10mm_cube()
stl_file = StlFile(stl_name)
# Or, create a ``BuildFile`` object.
build_file_name = examples.download_small_wedge_slm_build_file()
build_file = BuildFile(MachineType.SLM, build_file_name)
Select material#
Select a material. You can use the materials_list() method to
obtain a list of available materials.
print("Available material names: {}".format(additive.materials_list()))
Available material names: ['AlSi10Mg', 'Al357', 'CoCr', 'IN718', 'IN625', '316L', '17-4PH', 'Ti64']
You can obtain the parameters for a single material by passing a name
from the materials list to the material() method.
material = additive.material("17-4PH")
Specify machine parameters#
Specify machine parameters by first creating an AdditiveMachine object
and then assigning the desired values. All values are in SI units (m, kg, s, K)
unless otherwise noted.
machine = AdditiveMachine()
# Show available parameters
print(machine)
AdditiveMachine
laser_power: 195.0 W
scan_speed: 1.0 m/s
heater_temperature: 80.0 °C
layer_thickness: 5e-05 m
beam_diameter: 0.0001 m
starting_layer_angle: 57 °
layer_rotation_angle: 67 °
hatch_spacing: 0.0001 m
slicing_stripe_width: 0.01 m
heat_source_model: gaussian
ring_mode_index: 0
defocus: 0.0 m
Set laser power and scan speed#
Set the laser power and scan speed.
machine.scan_speed = 1 # m/s
machine.laser_power = 500 # W
Specify inputs for thermal history simulation#
Thermal history is simulated for the given geometry over a range of heights
in the Z dimension. More than one range can be specified. Each range is specified
with a Range object. The ranges are assigned to a CoaxialAverageSensorInputs
object, which also includes a sensor radius. The CoaxialAverageSensorInputs object
is assigned to a ThermalHistoryInput object.
# Values are in meters
sensor_inputs = CoaxialAverageSensorInputs(
radius=5e-4,
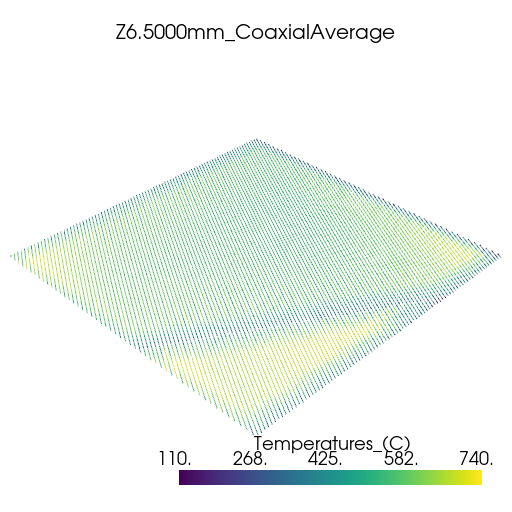
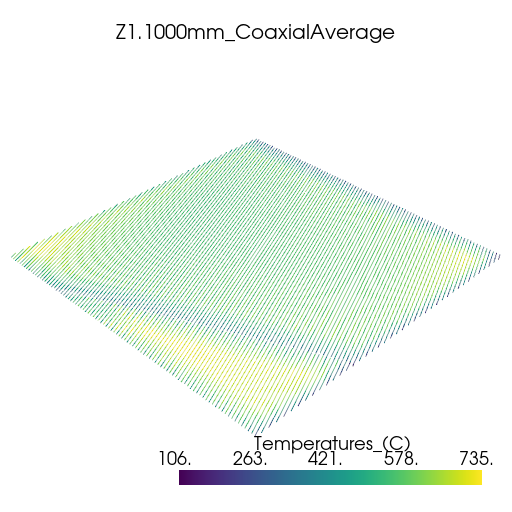
z_heights=[Range(min=1e-3, max=1.1e-3), Range(min=6.5e-3, max=6.6e-3)],
)
input = ThermalHistoryInput(
machine=machine,
material=material,
geometry=stl_file,
coax_ave_sensor_inputs=sensor_inputs,
)
Run simulation#
Use the simulate() method of the additive object to run the simulation.
The returned object is either a ThermalHistorySummary object or a
SimulationError object.
summary = additive.simulate(input)
if isinstance(summary, SimulationError):
raise Exception(summary.message)
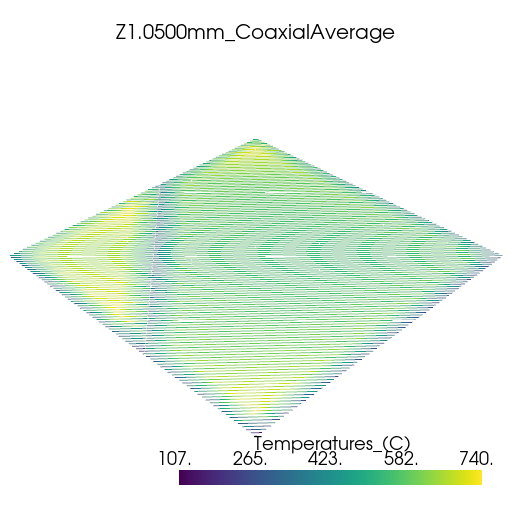
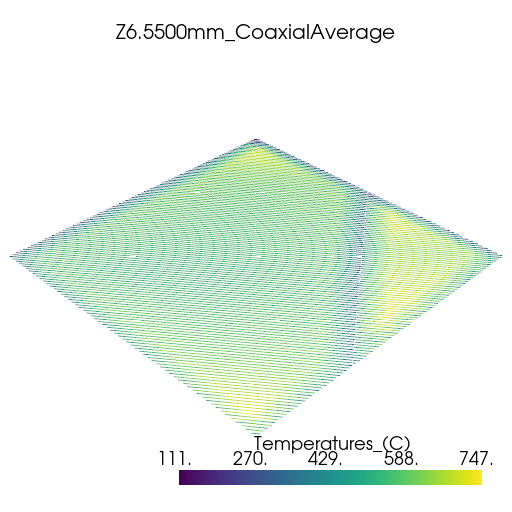
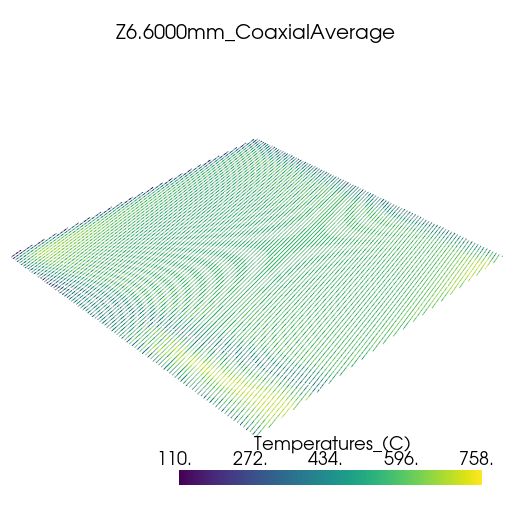
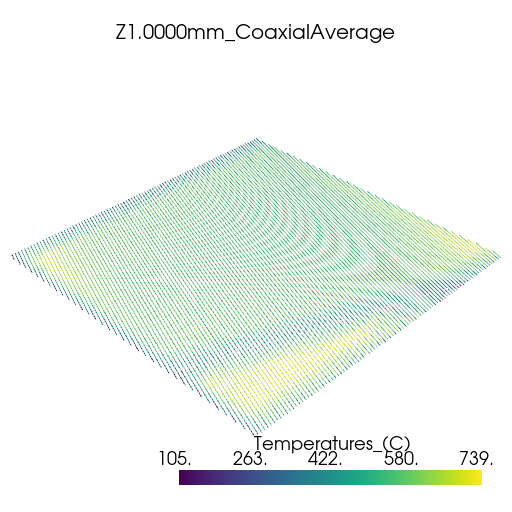
Plot thermal history#
Plot the thermal history using PyVista.
import glob
import os
import pyvista as pv
vtk_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(summary.coax_ave_output_folder, "*.vtk"))
for file in vtk_files:
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[512, 512])
plotter.add_mesh(pv.read(file))
title = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(file))[0]
plotter.add_title(title, font_size=8)
plotter.show()
Print the simulation logs#
To print the simulation logs, use the logs() property.
print(summary.logs)
Total running time of the script: (3 minutes 13.153 seconds)